How to Unit Test in Django
Django's test framework extends unittest.TestCase with django.test.TestCase, providing additional features like:
- Database Rollback: Each test runs in isolation with a separate test database.
- Client Simulation: You can simulate requests to views using self.client.
- Fixture Loading: You can load test data using fixtures.
Step 1 - Set up the Django project
- Install the necessary packages
pip install django djangorestframework
- Create a Django Project & App
django-admin startproject myproject
cd myproject
django-admin startapp products
- Add products and rest_framework to INSTALLED_APPS in myproject/settings.py.
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'rest_framework', # DRF
'products', # Products app
]
- Include the product url in the in myproject/urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('api/', include('products.urls')),
]
Step 2 - Create basic home page
- Edit products/views.pyand add a home function.
def home(request):
return HttpResponse("Hello, Django!")
- Add the home function to the urlpatterns in products/urls.py
path('', home, name='home'),
- Start the application
python manage.py runserver
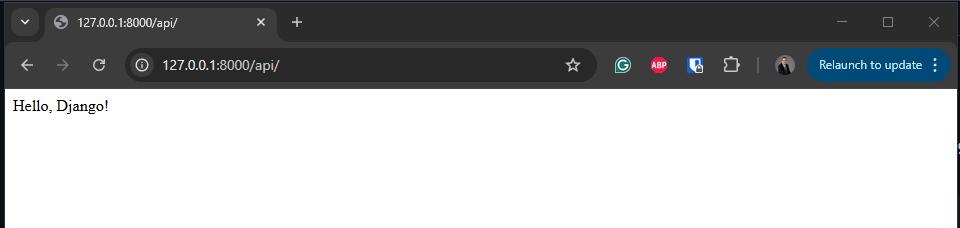
- With a web browser navigate to http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/ and confirm the page displays the text from the home function
Hello, Django!.
Step 3 - Unit test basic home page
To unit test the basic home page.
-
Create a new directory for the unit tests within the product app.
products/product_tests -
Inside the new directory create an empty file called products/product_tests/init.py
-
Create the file products/product_tests/test_home.py
from django.test import TestCase
from django.urls import reverse
from rest_framework import status
from rest_framework.test import APITestCase
from products.models import Product
class ProductAPITestCase(APITestCase):
def test_get_products(self):
"""Test confirms that the API home page display the text 'Hello, Django!'."""
# Arrange
home_url = reverse('home')
expected_response = "Hello, Django!"
# Act
actual_response = self.client.get(home_url)
# Assert
self.assertEqual(actual_response.status_code, status.HTTP_200_OK) # Check the status code to confirm the request was executed successfully
self.assertEqual(actual_response.content.decode(), expected_response) # Check the response content to confirm the expected text is displayed
- Execute the test unit
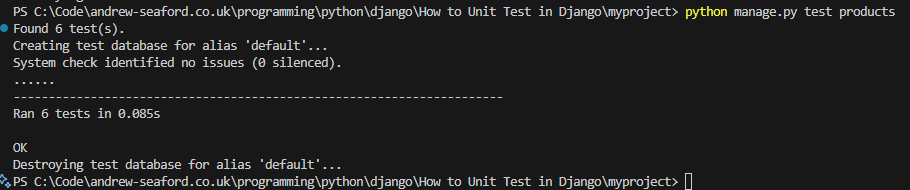
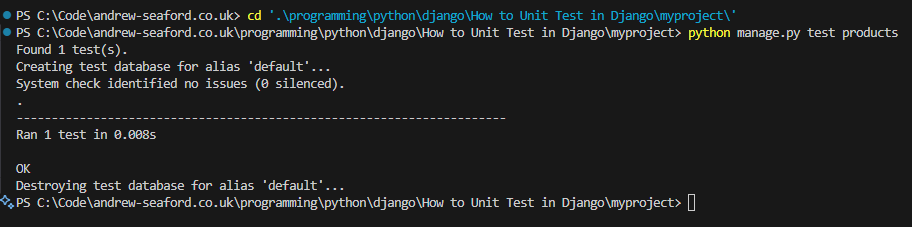
python manage.py test products
Step 4 - Create the API
- Define the Product Model in products/models.py. The model will store the data for the products, such as name and price.
from django.db import models
class Product(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=100)
price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=10, decimal_places=2)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
- Apply migrations:
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
- Create a Serializer. Create file products/serializers.py
from rest_framework import serializers
from .models import Product
class ProductSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Product
fields = '__all__'
- Create a ViewSet. Edit products/views.py
from rest_framework import viewsets
from .models import Product
from .serializers import ProductSerializer
from django.http import HttpResponse
class ProductViewSet(viewsets.ModelViewSet):
queryset = Product.objects.all()
serializer_class = ProductSerializer
def home(request):
return HttpResponse("Hello, Django!")
- Set Up URLs. Create file products/urls.py
from django.urls import path, include
from rest_framework.routers import DefaultRouter
from .views import ProductViewSet
from .views import home
router = DefaultRouter()
router.register(r'products', ProductViewSet)
urlpatterns = [
path('', home, name='home'),
path('', include(router.urls)),
]
Step 5 - Unit test the model
- Create a file for the model tests products/product_tests/test_models.py
from django.test import TestCase
from products.models import Product
class ProductModelTest(TestCase):
def test_create_product(self):
"""Test confirms that a Product instance is created correctly."""
# Arrange
name = "Laptop"
price = 1000.00
# Act
product = Product.objects.create(name=name, price=price)
# Assert
self.assertEqual(product.name, "Laptop")
self.assertEqual(product.price, 1000.00)
- Run the unit test.
python manage.py test products
Step 6 - Unit test the view
-
The following section will explain how to unit test and manually test the product view, using web browser and curl.
-
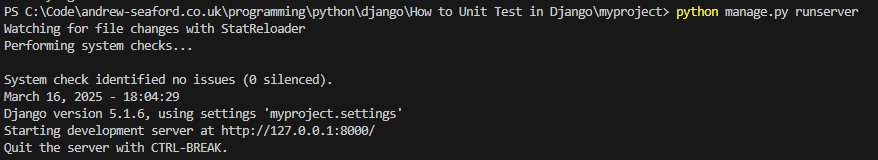
Run the site by executing
python manage.py runserver, so that you can manually test the API using cURL, Postman, or your browser.
Test Retrieving All Products (GET /api/products/)
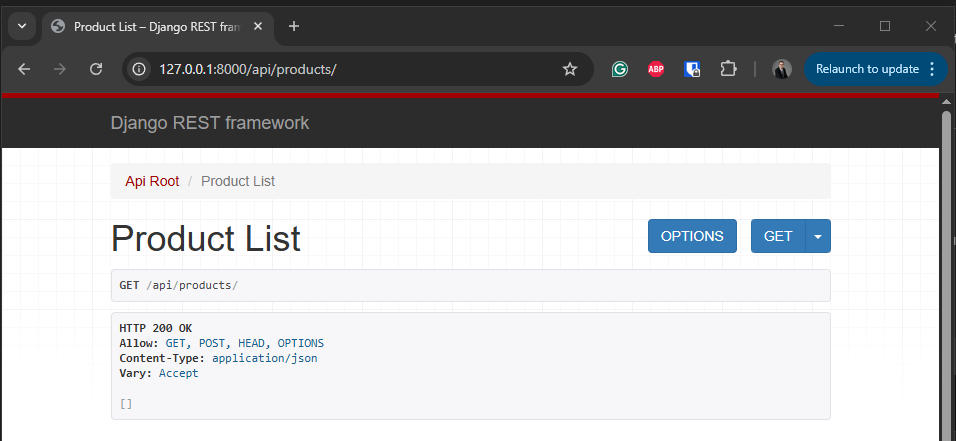
- To view a list of the products use a web browser to navigate to http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/products/, the list will be empty.
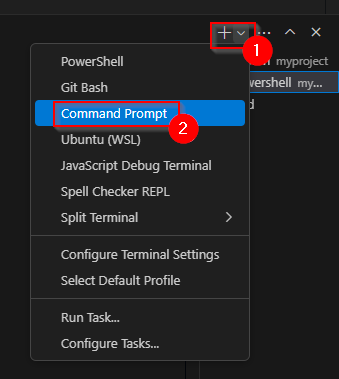
- To view the product list using curl execute a curl command from the CMD command prompt (PowerShell aliases curl to Invoke-WebRequest, which does not support the -X parameter). In VS Code, create the terminal by clicking the dropdown next to the plus icon, then select
Command Prompt.
curl -X GET http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/products/
- To unit test getting all products, create the file products/product_tests/test_view.py
from django.test import TestCase
from django.urls import reverse
from rest_framework import status
from rest_framework.test import APITestCase
from products.models import Product
class ProductAPITestCase(APITestCase):
def test_get_products(self):
"""Test confirms that the API returns a list of all products."""
# Arrange - No additional setup needed
# Act
response = self.client.get(self.list_url)
# Assert
self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_200_OK) # Check the status code to confirm the request was executed successfully
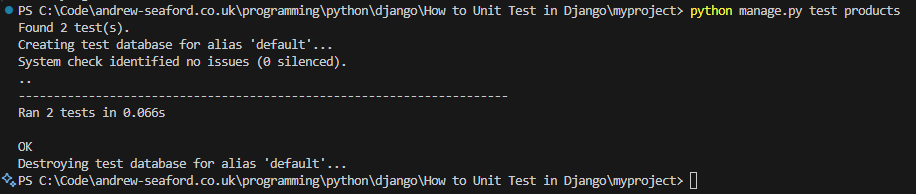
- Execute the tests
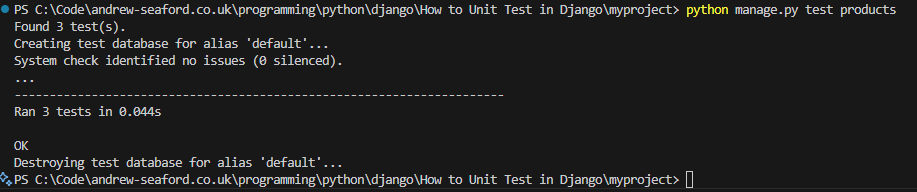
python manage.py test products
Test Creating a Product (POST /api/products/)
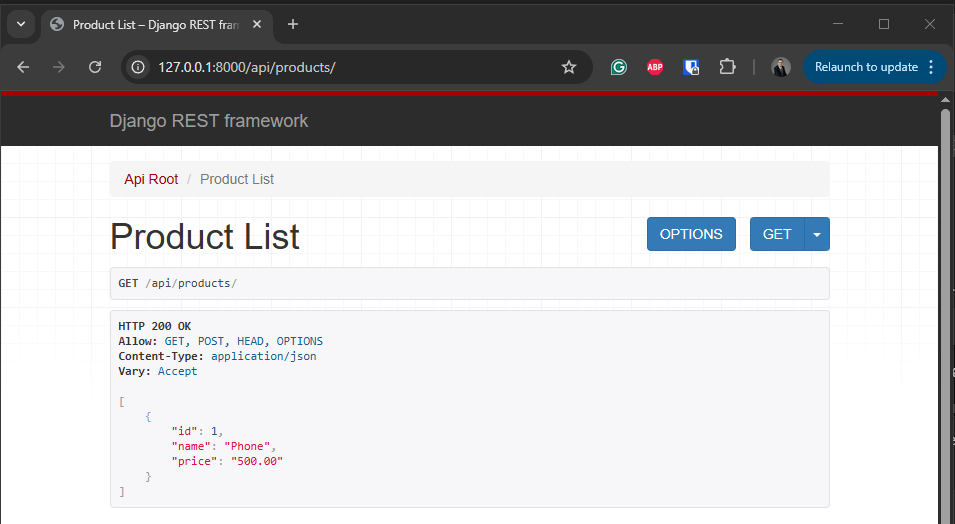
In the example we going to add a new product called Phone with the price 500.00. Execute a POST using curl, the response should return 201 Created. Then execute a second curl to get the list of products.
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/products/ -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{\"name\": \"Phone\", \"price\": 500.00}"
curl -X GET http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/products/
You can also browse http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/products/ to confirm the product was created.
To unit test, adding products, add the function test_create_product to products/product_tests/test_view.py
def test_create_product(self):
"""Test confirms that a new product can be created via API."""
# Arrange
data = {"name": "Phone", "price": 500.00}
# Act
response = self.client.post(self.list_url, data)
# Assert
self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_201_CREATED) # Check the status code to confirm a record was created
self.assertEqual(Product.objects.count(), 2) # Confirm the products list contains to items
- Run the tests
python manage.py test products
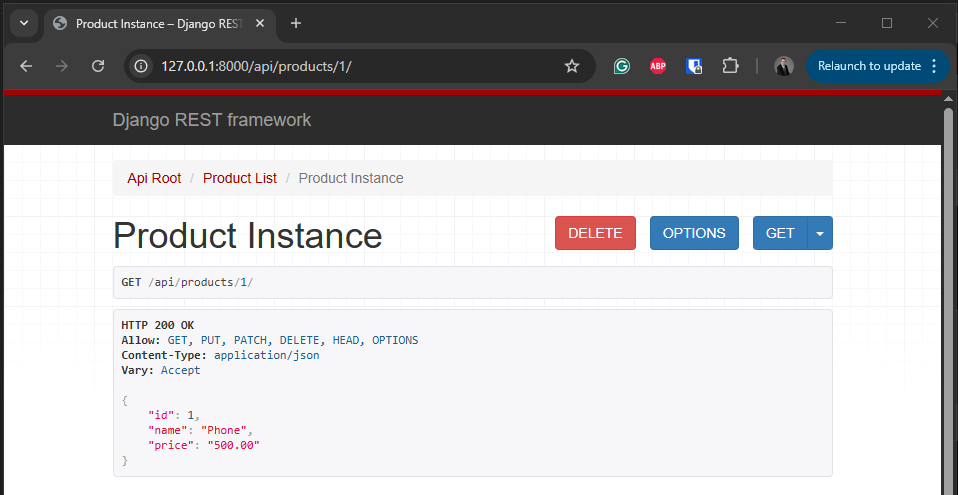
Test Retrieving a Single Product (GET /api/products/1/)
- To get a single products details, in this example we are going to get the details for the product, with product id 1. Execute curl to get the product details.
curl -X GET http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/products/1/
- or navigate to http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/products/1/
To unit test, adding products, add the function test_get_product_detail
def test_get_product_detail(self):
"""Test confirms that an individual product's details can be retrieved."""
# Arrange - Product is already created in setUp()
# Act
response = self.client.get(self.detail_url)
# Assert
self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_200_OK) # Check the status code to confirm the request was executed successfully
self.assertEqual(response.data['name'], "Laptop") # Check the products name
- Run the tests
python manage.py test products
Test Updating a Product (PUT /api/products/1/)
In this example, we are going to update the details for the product with the id 1. We going to change the name to Smartphone and the price to 600.00. Execute the PUT request using curl. The execute a second GET request for product 1 to confirm the product details have been updated.
curl -X PUT http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/products/1/ -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{\"name\": \"Smartphone\", \"price\": 600.00}"
curl -X GET http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/products/1/
- To unit test updating a product add the function
def test_update_product(self):
"""Test confirms that an existing product can be updated."""
# Arrange
data = {"name": "Smartphone", "price": 600.00}
# Act
response = self.client.put(self.detail_url, data)
# Assert
self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_200_OK)
self.product.refresh_from_db()
self.assertEqual(self.product.name, "Smartphone") # Confirm name change
self.assertEqual(self.product.price, 600.00) # Confirm price change
- Run the tests
python manage.py test products
Test Deleting a Product (DELETE /api/products/1/)
- To delete product id 1, execute DELETE request using curl, then execute a second curl request to confirm the product has been deleted.
curl -X DELETE http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/products/1/
curl -X GET http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/products/1/
To unit test deleting a product create the function def test_delete_product(self):
def test_delete_product(self):
"""Test confirms that a product can be deleted via API."""
# Arrange - Product exists (created by setup)
# Act
response = self.client.delete(self.detail_url)
# Assert
self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_204_NO_CONTENT)
self.assertEqual(Product.objects.count(), 0)
- Run the tests
python manage.py test products