Flood Fill using OpenCV
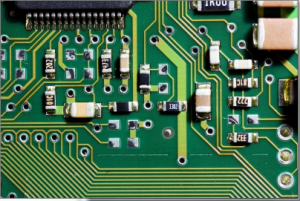
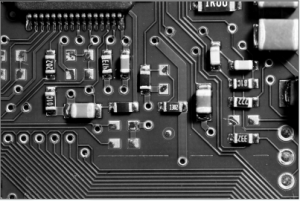
To use the flood fill, first a seed point is selected, then all neighbouring pixels of a similar colour are converted to a uniform colour. In this example the seed point is at 200, 200 (shown by a blue circle). The neighbouring pixels are then flood filled with a red colour.
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "cv.h"
#include "highgui.h"
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
// load the input image
IplImage* img = cvLoadImage("test.jpg");
// define the seed point
CvPoint seedPoint = cvPoint(200,200);
// flood fill with red
cvFloodFill(img, seedPoint, CV_RGB(255,0,0), CV_RGB(8,90,60), CV_RGB(10,100,70),NULL,4,NULL);
// draw a blue circle at the seed point
cvCircle(img, seedPoint, 3, CV_RGB(0,0,255), 3, 8);
// show the output
cvNamedWindow("Output", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cvShowImage("Output", img);
// wait for user
cvWaitKey(0);
// save image
cvSaveImage("output.jpg",img);
// garbage collection
cvReleaseImage(&img);
cvDestroyWindow("Output");
return 0;
}