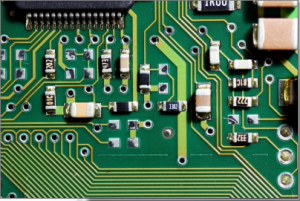
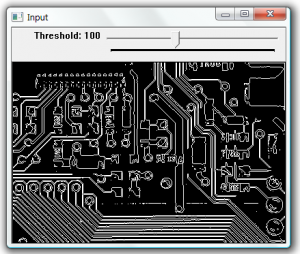
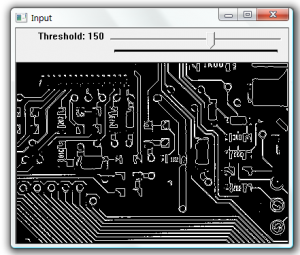
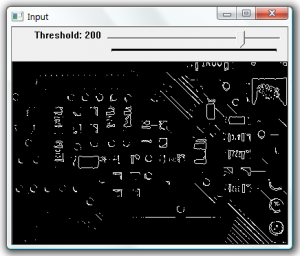
To detect the dominant points within an image first we must find the edges. In this example the edges are found using cvFindContours. The resulting contours are then processed to find the dominant points along the contour. This is done using the cvFindDominantPoints function, this function implements the IPAN99 algorithm to find the points. A small circle is then drawn at each dominant point.
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "cv.h"
#include "highgui.h"
#include "cvaux.h"
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
// open and display input image
IplImage* input = cvLoadImage("test.jpg", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
cvNamedWindow("Input", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cvShowImage("Input", input);
// create gray scale image for edge detection
IplImage* edge = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(input), 8,1);
// create output image
IplImage* output = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(input), 8,1);
// threshold the input image
cvThreshold(input, edge, 230,255, CV_THRESH_BINARY);
cvNamedWindow("Threshold", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cvShowImage("Threshold", edge);
// generate the contours
CvMemStorage* storage = cvCreateMemStorage();
CvSeq* contours = NULL;
int Nc = cvFindContours(edge, storage, &contours, sizeof(CvContour), CV_RETR_LIST);
// diplay the contours
printf("Total contours found = %d\n", Nc);
cvDrawContours(output, contours, cvScalarAll(255),cvScalarAll(255),10);
// generate the dominant points
CvMemStorage* dominantstorage = cvCreateMemStorage();
CvSeq* dominant = cvFindDominantPoints(contours, dominantstorage, CV_DOMINANT_IPAN,5,15,5,170);
printf("dominant total=%d\n", dominant->total);
// display the dominant points
int i, idx;
CvPoint p;
for ( i = 0; i < dominant->total; i++)
{
idx = *(int *) cvGetSeqElem(dominant, i);
p = *(CvPoint *) cvGetSeqElem(contours, idx);
cvDrawCircle( output, p , 1, CV_RGB(255,0,0) );
printf("%d %d %d\n", idx, p.x, p.y);
}
// show output
cvNamedWindow("Output", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cvShowImage("Output", output);
// wait for user
cvWaitKey(0);
// garbage collection
cvReleaseImage(&input);
cvDestroyWindow("Input");
cvReleaseImage(&edge);
cvDestroyWindow("Threshold");
cvReleaseImage(&output);
cvDestroyWindow("Output");
return 0;
}
 Input Image |
 After threshold |
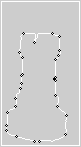 Output |